Domain owners and resellers who leverage SEO to impact the value of their digital portfolio should be well aware of what elements are foundational for SEO with AI, and how the ongoing revolution is affecting the search industry.
The web goes buzzing on how SEO as we know it is dead: some mediums, tools and surface-level mechanics are indeed shifting, yet, as we’ll explore in this article, the foundational logics of organic positioning haven’t quite changed.
Still, to be prepared for the AI revolution and ride the change profitably, it’s important to understand where and how LLMs differ from traditional search engines and to grasp the current status of the search landscape itself.
Table of content
- Intent parallels – Understanding the core search functions of SEO and LLMs
- The search market today: Google’s hegemony
- EMDs and one-word domain names vs query matching
- The GEO acronym and the SERP of AI
- The AI search landscape by demography
- Domain value assessment through AI algorithms
- The rise of AI-specific domain extensions
- Tracking AI-based traffic
- Riding the new SEO panorama: takeaways for domain owners
Intent parallels – Understanding the core search functions of SEO and LLMs
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and Large Language Models (LLMs) operate in parallel yet distinct ways.
SEO is designed to help search engines rank and serve web content efficiently, whereas LLMs focus on understanding and generating text-based responses.
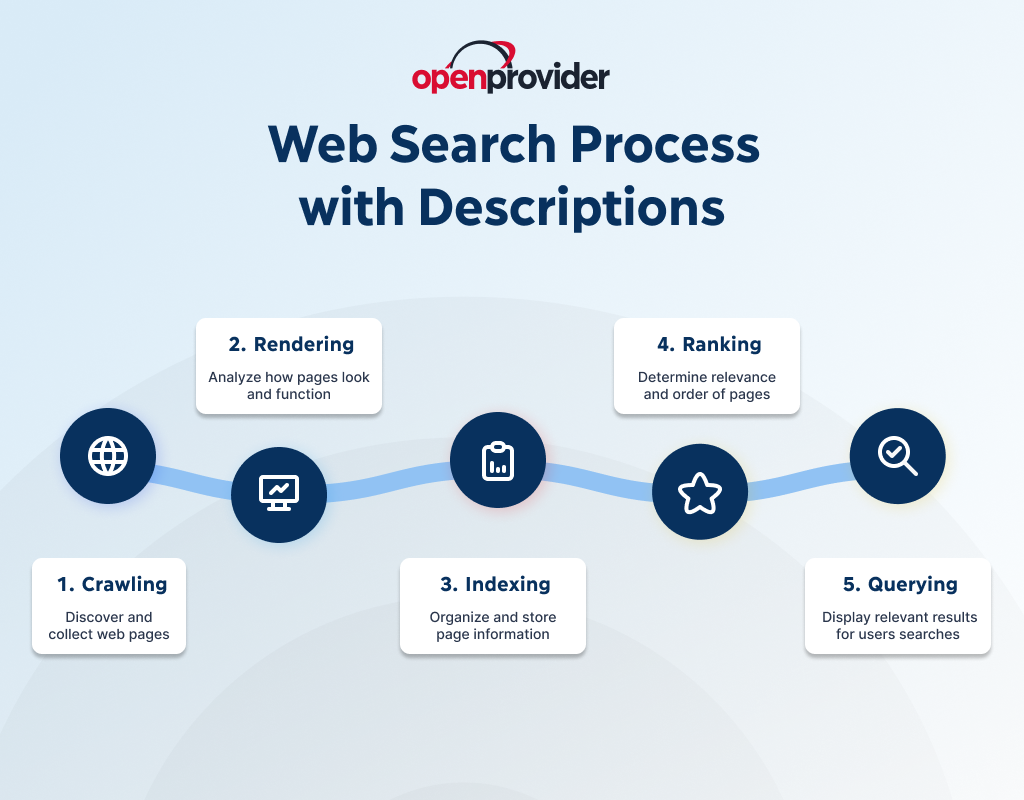
1. Discovery phase
SEO
This phase is about focusing on crawling and indexing web pages across the internet, gathering and storing data primarily through automated bots.
LLMs
Large Language Models process and encode vast amounts of textual data from various sources, including scraped websites, research papers, and public repositories, to develop a structured knowledge base.
2. Identification
SEO
With the indexing step, search engines need to determine which pages are most relevant for a given search query. This identification process relies on keyword analysis, metadata, and user engagement signals.
LLMs
Instead of scanning live web pages, they retrieve knowledge from their pre-trained data and structured language models.
3. Classification
SEO
Traditional algorithms classify content by analyzing its quality, relevance, and authority. They interpret the meaning of words and their context. This allows them to distinguish between similar phrases and categorize web pages based on search intent.
LLMs
LLMs classify information differently, focusing on context and semantic relationships to generate coherent responses. Instead of ranking pages, they organize data into logical categories to produce human-like text.
4. Scoring
SEO
Domain owners know that search engines rank web pages based on a scoring system that considers relevance, authority, and usability. Pages with high-quality backlinks, strong domain authority, and well-optimized content score higher in rankings, increasing their visibility in search results.
LLMs
LLMs, however, assign probabilities to potential responses instead of ranking pages. Unlike SEO, where the best-ranked web pages are surfaced, LLMs generate responses based on likelihood, producing text that reflects the patterns found in their dataset.
The search market today: Google’s hegemony
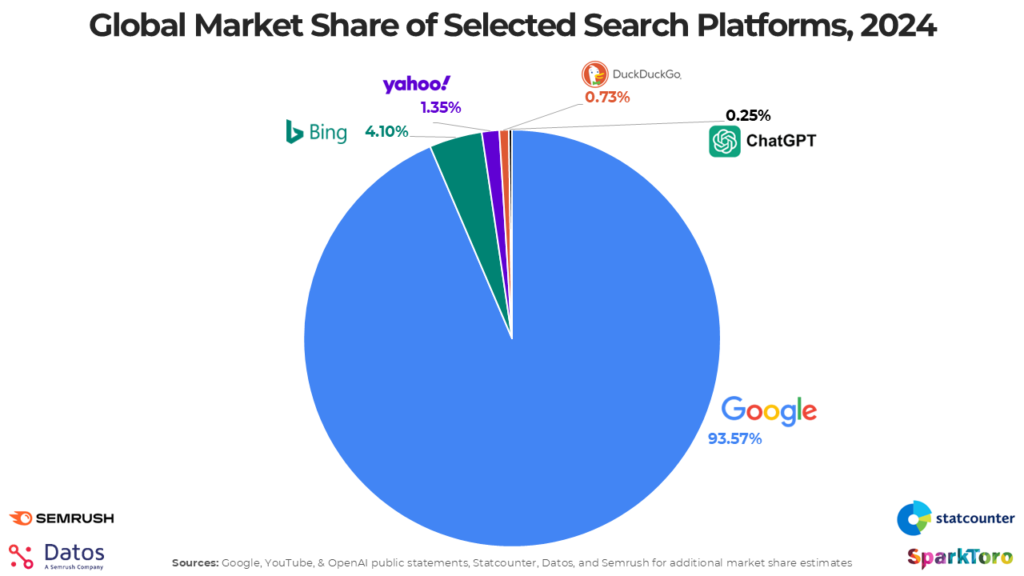
In case you’re in doubt, Google is still the predominant player of search.
In fact, according to a research published by SparkToro in March 2025 (after a collaborative effort), we observe it occupying 93,57% of the global search market, with an estimate of 14 billion searches per day.
Grasping the search derivatives of Google AIO
This said, the word “Google” does not represent traditional search only.
Google AIO (AI Overviews) is the Gemini-based asset of Alphabet for AI search: several players in the SEO world have analyzed – and keep studying – the behavior of its non-deterministic algorithms, identifying how it impacts the SEO panorama.
Here are some key points:
- Google AIO affects more than 100 extra-European countries
- The results triggered by Google AIO are mainly subject to long tail queries (at least 4 words)
- The queries that seem to trigger Google AIO the most have low search volume (less than 1000 according to Semrush)
- Search intents related to Google AIO are primarily informational; as per Ahrefs:
- Informational: 99.2% (AIO) vs. 94.2% (Non-AIO)
- Navigational: 20.3% (AIO) vs. 33.7% (Non-AIO)
- Commercial: 5.8% (AIO) vs. 14.9% (Non-AIO)
- Transactional: 4% (AIO) vs. 4.7% (Non-AIO)
- There are several industries majorly involved in Google AIO results; different studies show us some overlaps, but if you are targeting a specific niche for your domain assets, or if you are a web agency with clients in some of the sectors listed below, you can use the following data to offer industry-specific Google AIO recommendations.
SEranking observes that the following ones trigger most of the AIO results:
- Relationships: over 26%
- Food and Beverage: over 24%
- Technology: about 18%
While Semrush reports Health, People & Society, and Science for desktop AIO results and People & Society, Science and Food & Drink on mobile.
Finally, BrightEdge identifies Healthcare, Education and B2B Tech as top 3 industries present in Google AIO.
Top domain ranking for keywords does not correspond to AIO top results
Furthermore, several studies agree on the fact that domains displayed in the SERP after a traditional search do not correspond to the ones mentioned after a Google AIO result is triggered.
Semrush observes that:
- Less than 50% of AI overviews link to the first top organic result;
- Between 25% and 38% of AI overviews entirely skip the top 3 organic results;
This is regardless of the domain rating or authority score, which means that domain resellers looking to position their assets on top of AI-generated results have to diversify their strategies.
The majority of the studies, trials and experiments devoted to this purposes are, indeed, experiments: the SEO industry is still figuring out how to crack the code of AI-generated results, but most of the players out there have already introduced both ways to measure AI-based traffic and tactics to favour domain positioning via AI.
As we’ll see later in this article, some of these are general “rules” that are taking shape, while other examples saw tactics that would not normally be allowed to run in the search panorama.
AI apps
Other AI search engines and their AI tools like Bing (Copilot), Duckduckgo (Duck.ai), and ChatGPT (after its prototype SearchGPT) have a small chunk of the search market pie, with ChatGPT leading the AI game.
In fact, about 30% of the prompts inputted in OpenAI’s famous tools have a search intent (although we are still talking of low relative numbers, about 37 and a half million searches per day).
So, the role of AI apps in search is still in its embryonic phase: Chat GPT, Anthropic’s Claude, X’s Grok and other tools are certainly paving the way for additional types of searches, where users look for direct, tailored answers rather than a list of “least-worst-links” to click on.
EMDs and one-word domain names vs query matching
All this considered, if we think of one-word domain names used to not only be catchy, but also perform well in short queries searches, the dynamic is obviously shifting.
Exact match domains (EMDs) that precisely matched search queries were believed to have a strong advantage in search engine rankings.
Long, specific queries are predominant in the era of AI search so, although single-worded domains can still constitute an excellent asset, the current consensus is that the quality of website content, user experience, backlinks, and other factors play a stronger role in SEO.
The GEO acronym and the SERP of AI
GEO stands for Generative Engine Optimization and it’s one of the emerging terms related to SEO work for AI-based search engines.
Under the umbrella of GEO and organic domain optimization in the AI era, we can identify some axioms that are taking more and more the form of principles.
AI don’t value the size of the domain
The main purpose of a generative AI is to return an output that is as useful and accurate as possible for the user.
And, as we know, the most popular domain is not necessarily the one with the best answer.
Thus, we expect and observe AI search engines and applications to favor the most contextual source (or the one that most closely matches an appropriate answer, probabilistically speaking).
The authority and the popularity of a domain can still count, but it’s the structure, content and context of a certain page that seems to determine the display of a domain versus another.
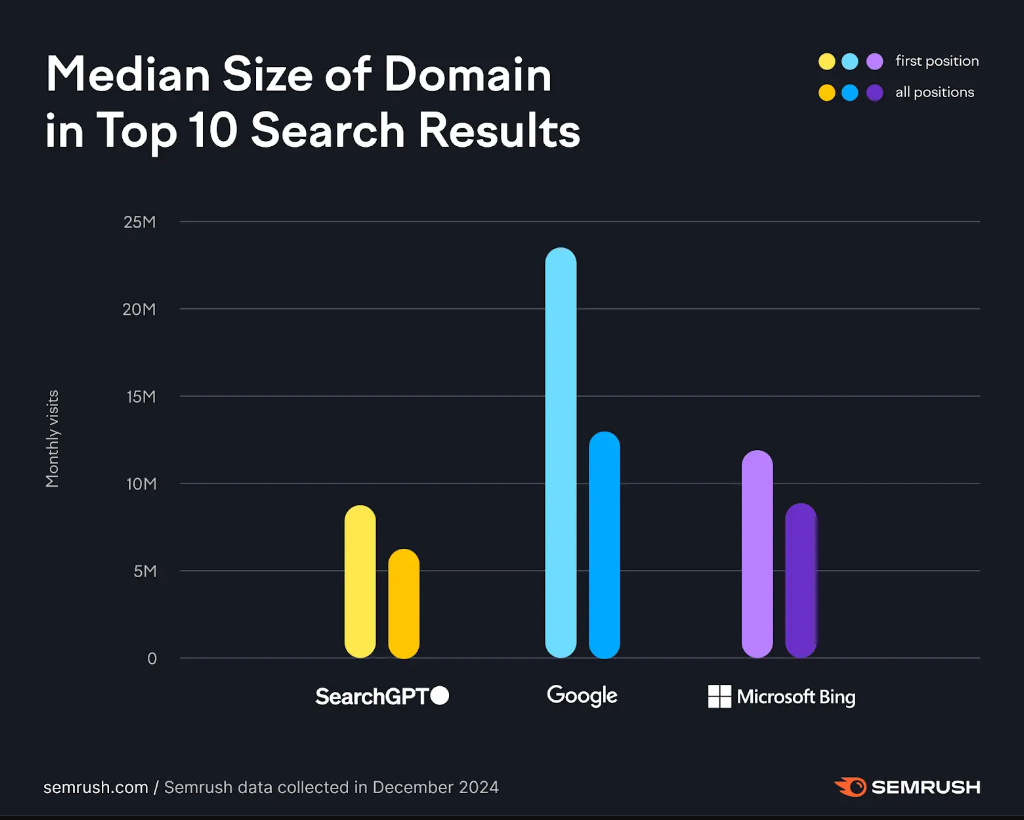
In fact, let’s look at these breakdowns.
ChatGPT tends to return smaller domains
After an analysis of about 5000 queries, Semrush found that ChatGPT is prone to display domains with less than 10 million visits in the top 10 results.
AI Overviews investigates lower-ranking pages
As observed by BrightEdge, AI Overviews can prioritize organic results pulling information from low-ranking results in order to generate more contextual responses.
This confirms that AI search engines are bringing opportunities to less powerful domains – as long as the content in them is adequate and matches the query intent and context –.
Technical SEO is growing in importance
Getting a referral by AI firstly means being recognizable by it. As explained before, LLMs have their own process to discover and identify a domain and its content.
This means that elements like structured data, schema markups, meta elements and content hierarchies can play a game-changing role.
As Matt G. Southern says in a recent article published in the Search Engine Journal:
“Not long ago, technical SEO mostly meant handling sitemaps, robots.txt files, and basic schema markup. Now, we’re writing about JavaScript rendering, Core Web Vitals, and AI content evaluation.”
The AI search landscape by demography
When talking about search, Gen Z is the demographic segment that most uses AI.
Analyzing user behavior with search engines since ChatGPT became popular in 2022, GWI has gathered the following statistics about how different generations perform searches (top 3 tools for each cluster).
Gen Z
- Manual search engines (e.g. Google, Yahoo!) – 58%
- Social media platforms – 46%
- AI platforms/chatbots (e.g. ChatGPT, Bard) – 31%
Millennials
- Manual search engines (e.g. Google, Yahoo!) – 61%
- Social media platforms – 46%
- Smartphone voice assistants (e.g. Siri) – 31%
Gen X
- Manual search engines (e.g. Google, Yahoo!) – 73%
- Social media platforms – 37%
- Brand/retail platforms (e.g. Amazon) – 26%
Baby boomers
- Manual search engines (e.g. Google, Yahoo!) – 76%
- Brand/retail platforms (e.g. Amazon) – 22%
- Social media platforms – 21%
Domain value assessment through AI algorithms
The same valuation and appraisal processes for domains has evolved considerably with AI.
As domain appraisal systems have AI algorithms ingrained, domain owners now rely on them to assess potential domain purchases based on comprehensive data analysis rather than relying solely on traditional metrics like traffic and backlinks.
The rise of AI-specific domain extensions
The digital landscape has witnessed a significant shift in domain extension preferences, particularly with the meteoric rise of .ai domains.
As we explore in this article, domain owners are increasingly recognizing the strategic value of these extensions, not just for branding purposes but also for SEO advantages in an AI-dominated future.
This trend reflects a deeper understanding of how domain choices impact search visibility in the age of intelligent algorithms.
Tracking AI-based traffic
As AI-driven traffic grows, business and domain owners must start monitoring it.
AI search engines often lack UTM parameters in their links—Google AIO never includes them by default, while ChatGPT does occasionally. Consequently, GA4 tracks AI traffic as direct (from AI apps) or referral (if source data is present).
To identify AI-driven traffic, domain owners can apply filters, set up regex rules, or create exploration charts that track AI-related referrers.
These shifts impact domain valuations, emphasizing holistic performance across voice, visual, and conversational search rather than just SEO compliance with Google AIO’s evolving algorithms.
To stay competitive and bridge traffic gaps, domain owners should combine Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) strategies with automated portfolio management for efficiency and growth.
Riding the new SEO panorama: takeaways for domain owners
Finally, domain resellers can follow these SEO strategic tips for efficient domain portfolio management that can perform well within the search landscape in the AI era.
- Search engines should be able to recognize and index your domains. Optimize domain landing pages with proper indexing, canonical tags, and structured data to enhance AI and search engine visibility.
- Keep establishing a clear value proposition for each domain, by highlighting the unique selling points of your domains, including premium features, industry relevance, and potential use cases.
- AI-based SEO strategies and GEO tactics refer to a small chunk of the search panorama, yet they are key to position domains that would normally not rank in traditional SERP.
- Domain authority is less important but still counts. Get listed in domain marketplaces and industry directories by submitting domains to top domain marketplaces (Sedo, Afternic, Dan.com) and ensure visibility in relevant directories.
- Domain owners can create AI-optimized press releases and content together with structured data related to their domain content. This serves to increase discoverability in AI-generated search results.
- Information is key: stay updated and collaborate with SEO experts and digital entrepreneurs, engaging with domain investors, niche communities and forums, hosting companies, and tech influencers to expand your reach and improve domain demand.
Rely on secure providers that are aware of the AI panorama, and look for domain platforms that allow you to buy and manage domains in bulk, including .AI extensions